Adenine treatment triggers renal injury and causes morphological, biochemical and histopathological alterations which mimic human CKD. Studies in mice have shown that adenine causes renal functional impairment, activation of myofibroblasts, inflammatory responses and ECM accumulation leading to interstitial fibrosis within 28 days. Triangulum Biopharma offers adenine induced CKD with severe anemia and renal interstitial fibrosis in mice for preclinical efficacy, proof-of-concept and mechanism of action studies. In addition, Triangulum Biopharma also conducts comprehensive clinical chemistry for the plasma/serum bio-markers, hematocrit, plasma erythropoietin, ferritin measurements, cytokine analysis, biochemical and ELISA assays, gene expression analysis by qPCR, renal hydroxyproline assays and comprehensive histopathology evaluation.
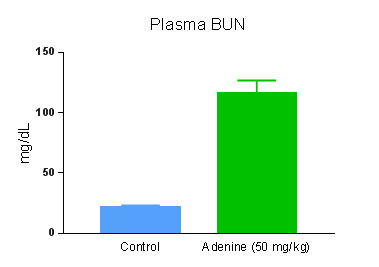
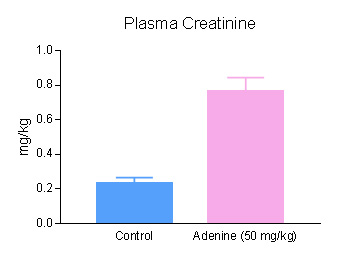
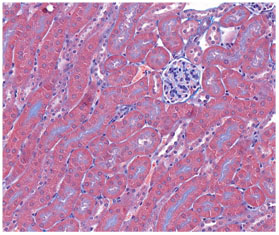
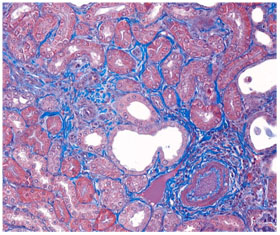
Histopathology of kidney treated with control and Adenine (50 mg/kg) daily for 28 days. The sections were stained with Masson's Trichrome to visualize fibrosis.